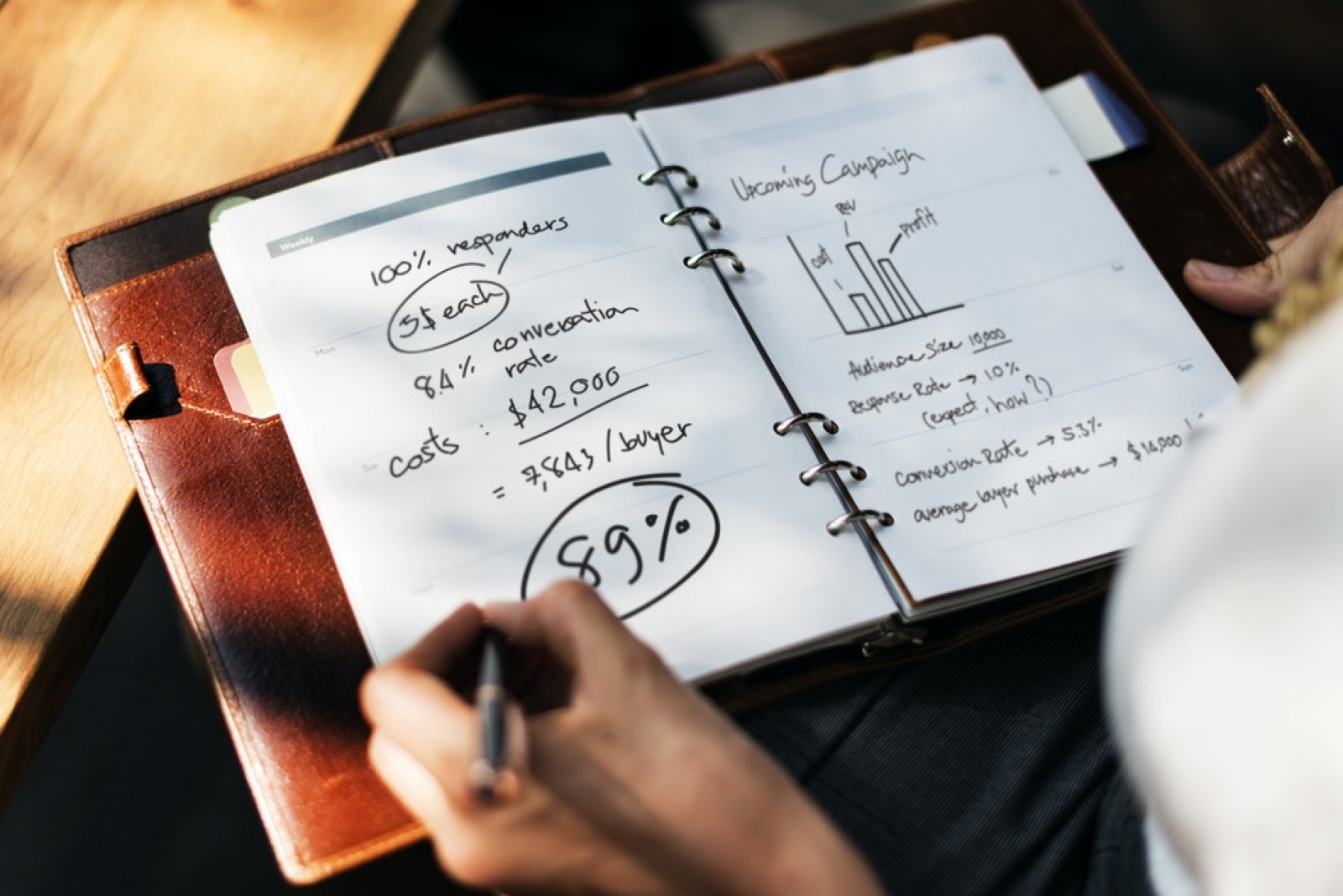
French mortgage rates have reached record lows in recent years, in line with the lowering of Euribor rates. In February 2018, average borrowing rates remained very low at 1.61% (according to Banque de France data. Unlike some other European countries, very long fixed-term mortgages in France (15, 20 years) are quite common as buyers look to lock in the best rates.
As France continues to stabilise its economy, the best French mortgage rates are still typically given to those with bigger deposits and shorter repayment periods. To give an example, for €100,000 borrowed the monthly cost would be around €513 for a 20-year, fixed-rate mortgage (at 2.15%).
Loan offer
A real estate loan is used for purchase of a residential (or professional and residential) real estate, or land intended for construction. A traditional home loan is offered by a bank to the household that wishes to carry out a real estate transaction. This type of loan can be used only for the purchase of housing or land.
Object
A real estate loan is offered by a bank to carry out a real estate transaction. This type of loan makes it possible to finance, the following:
-
the acquisition of housing and the performance of repair, improvement or maintenance of the building thus acquired;
-
the acquisition of land for the construction of a dwelling;
-
the construction of a dwelling;
-
the acquisition of shares in real estate companies.
The formulas offered by the lending institutions are different and take into account the income of the borrower.
NB: a credit granted to finance only expenses for the repair, improvement or maintenance of a residential complex is considered as a consumer credit when it is not secured by any bank guarantee or other comparable security.
Duration
The term is variable, usually negotiated between the borrower and the loan provider. Thus, the average duration of a loan is 20 to 25 years but can sometimes go up to 30 or 35 years.
Amount
There is no maximum amount. However, the value of the loan usually depends on the amount of the borrower's resources.
Rate
The interest rate is defined by the loan provider. It can be:
-
a fixed rate, which will not change during the term of the loan;
-
a variable rate, which progresses over time or according to an index (for example: the interbank rate of the euro zone).
-
Lending institutions have different rates. You are free to compare these rates.
NB: even if the rate of your loan is fixed, it is generally possible to renegotiate the current loan to obtain better conditions.
Guarantees
The lender may require guarantees for the loan. The following documents can be demanded:
-
a bank guarantee,
-
a mortgage of the property.